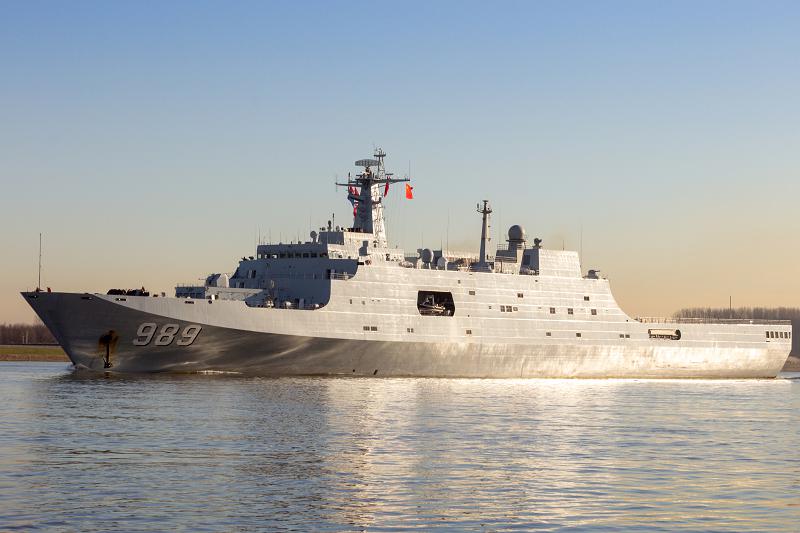
ROTTERDAM - JAN 30, 2015: Chinese People s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) amphibious transport ship 989 Changbai Shan (NATO name: Yuzhao) leaving the Port of Rotterdam after the first visit ever of the Chinese Navy to The Netherlands
ROTTERDAM - JAN 30, 2015: Chinese People s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) amphibious transport ship 989 Changbai Shan (NATO name: Yuzhao) leaving the Port of Rotterdam after the first visit ever of the Chinese Navy to The Netherlands
DoD’s 2000 report assessed that the PLA was slowly and unevenly adapting to the trends in modern warfare. The PLA’s force structure and capabilities focused largely on waging large-scale land warfare along China’s borders. The PLA’s ground, air, and naval forces were sizable but mostly obsolete. Its conventional missiles were generally of short range and modest accuracy. The PLA’s emergent cyber capabilities were rudimentary; its use of information technology was well behind the curve; and its nominal space capabilities were based on outdated technologies for the day. Further, China’s defense industry struggled to produce high-quality systems. Even if the PRC could produce or acquire modern weapons, the PLA lacked the joint organizations and training needed to field them effectively. The report assessed that the PLA’s organizational obstacles were severe enough that if left unaddressed they would “inhibit the PLA’s maturation into a world-class military force.”
Two decades later, the PLA’s objective is to become a “world-class” military by the end of 2049—a goal first announced by General Secretary Xi Jinping in 2017. Although the CCP has not defined what a “world-class” military means, within the context of the PRC’s national strategy it is likely that Beijing will seek to develop a military by mid- century that is equal to—or in some cases superior to—the U.S. military, or that of any other great power that the PRC views as a threat. As this year’s report details, the PRC has marshalled the resources, technology, and political will over the past two decades to strengthen and modernize the PLA in nearly every respect. Indeed, as this report shows, China is already ahead of the United States in certain areas such as:
- Shipbuilding: The PRC has the largest navy in the world, with an overall battle force of approximately 350 ships and submarines including over 130 majorsurface combatants. In comparison, the U.S. Navy’s battle force is approximately293 ships as of early 2020.
- Land-based conventional ballistic and cruise missiles: The PRC has more than 1,250 ground-launched ballistic missiles (GLBMs) and ground-launched cruise missiles (GLCMs) with ranges between 500 and 5,500 kilometers. The United States currently fields one type of conventional GLBM with a range of 70 to 300 kilometers and no GLCMs.
- Integrated air defense systems: The PRC has one of the world’s largest forces of advanced long-range surface-to-air systems—including Russian-built S-400s, S-300s, and domestically produced systems—that constitute part of its robust and redundant integrated air defense system architecture.
Source: Office of The Secretary Of Defense Annual Report to Congress: Military and
Security Developments Involving the People’s Republic of China
Published by permission of DOD.